

However, there is still much more to learn with Postgres. To complete this process, you will require a working installation of the CentOS 7 operating system with root privileges and a text editor of your choice. You have learned how to set up PostgreSQL13 on your CentOS 7 server. # INSERT INTO employees VALUES ('Adam','Pipo') Ĩ- Query all rows from the table named employees: # SELECT * FROM employees ĩ- Exit from PosgreSQL prompt: # \q Conclusion Access the PostgreSQL Database Server:ģ- Create a new PosgreSQL Database named yallalabs: # CREATE DATABASE yallalabs Ĥ- Connect to an existant PosgreSQL database named yallalabs: # \c yallalabsĥ- Create a table named employees: # create table employees (name varchar(25), surname varchar(25)) ħ- Insert a couple of rows into the new table named employees: # INSERT INTO employees VALUES ('Lotfi','Waderni') Installation PostgreSQL 13ġ- Add the PostgreSQL repository: $ sudo yum install -y Ģ- Install PostgreSQL 13: $ sudo yum install -y postgresql13-serverģ- Initialize the database: $ sudo /usr/pgsql-13/bin/postgresql-13-setup initdbĤ- Enable and start the PostgreSQL service: $ sudo systemctl enable -now postgresql-13ġ- PostgreSQL by default creates a user named postgres. In this article, we are going to show you how to install PostgreSQL 13 database on CentOS 7.
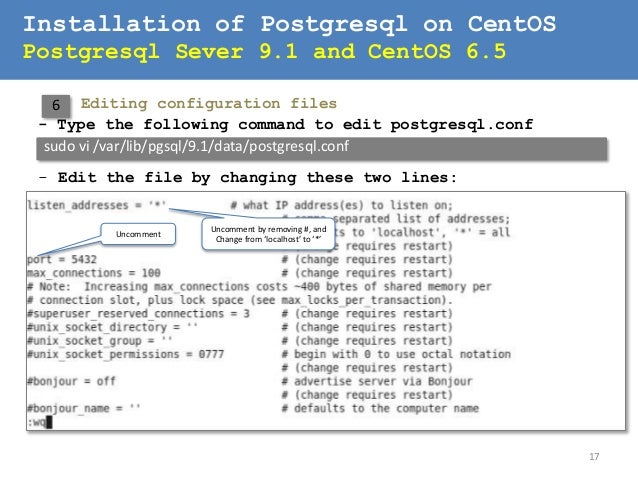
Unlike other relational database systems, PostgreSQL allows users to create unique operators, complex data types, aggregate functions, data type conversion character, and other various database objects through the SQL function. PostgreSQL is a powerful, open source object-relational database system ( ORDBMS ).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
